 About Cord Tissue
About Cord TissueCord tissue contains blood vessels supported by tissue called Wharton’s jelly, which is a rich source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). The surrounding tissue is also a rich source of other cell types, e.g., endothelial cells, which have different potential uses.
MSCs collected from cord tissue are multi-potent, meaning they have the ability to regenerate and differentiate into many different types of cells including cartilage, bone, fat and muscle. This important characteristic means that they could potentially be used to treat more conditions than cord blood alone can treat4.
There are more than 40 studies currently investigating the role of cord tissue MSCs in a wide variety of conditions including; stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, cartilage injury and cerebral palsy.
While cord tissue is not currently approved for clinical therapies, many clinical trials are underway around the world.
|
Pre-clinical research |
Clinical trials |
| Parkinson's disease | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Multiple sclerosis |
| Stroke | Osteoarthritis |
| Type 1 diabetes | Liver transplantation |
| Liver fibrosis | Asthma |
| Lung cancer | Burns |
| Cartilage | Lupus |
| Cerebral palsy |
Find out more about trials and research involving cord tissue.
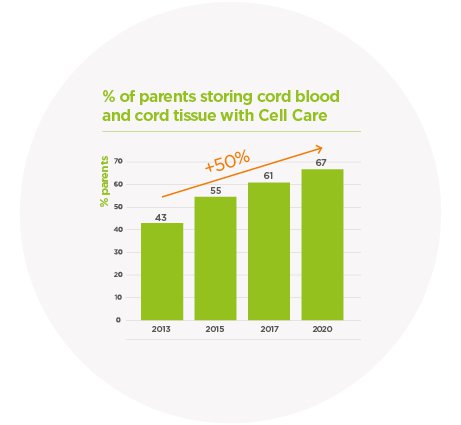
Umbilical Cord tissue banking is now commonplace with over 65% of Cell Care customers electing to store both cord blood and cord tissue23.
In some parts of the world, this proportion is as high as 68%24. This is steadily growing as awareness of the future potential of MSCs and other cord tissue cells expands.
|
Cell Care’s Process |
Description |
|
Stores an entire segment of umbilical cord tissue |
|
|
Stored in 5 cryo-vials |
|
|
First to collect and store cord tissue in Australia |
|
|
Most experience collecting cord tissue |
|
|
Our quality process |
|
|
Low deposit |
|
Cell Care stores an entire segment of the cord tissue. Unlike other companies who extract only the MSC’s from cord tissue, all cell types are stored including mesenchymal stem cells, endothelial cells and epithelial cells. All 6 regions are stored: Wharton’s jelly, intervascular region, perivascular region, sub-amniotic region, blood vessels and amniotic epithelium. Should future cell therapies be developed using any of the cord tissue cell types, Cell Care clients will have stored these relevant cells.
Cell Care stores cord tissue in 5 cryo-vials. This may allow the potential for cord tissue to be used in multiple therapeutic treatments and alternate samples to be thawed at different times.
Cell Care was the first private cord blood bank to introduce cord tissue storage in Australia. Cell Care worked closely with scientists from Monash Institute of Medical Research to build a dedicated cord tissue laboratory. Cell Care has stored over 10,000 cord tissue samples since this service was launched in April 2012.
Cell Care offers a low deposit of $250 for cord blood and tissue storage.
As labour and birth can be unpredictable, in the event that your cord tissue is not collected at the time of birth, there is no charge for this service. The deposit will be offset against any costs of cord blood storage.
Cell Care collects, processes and stores umbilical cord tissue in line with the Australian code of Good Manufacturing Process. In the event that umbilical cord tissue is approved for therapeutic use, Cell Care would be in a position to apply for a retrospective licence for all samples stored.